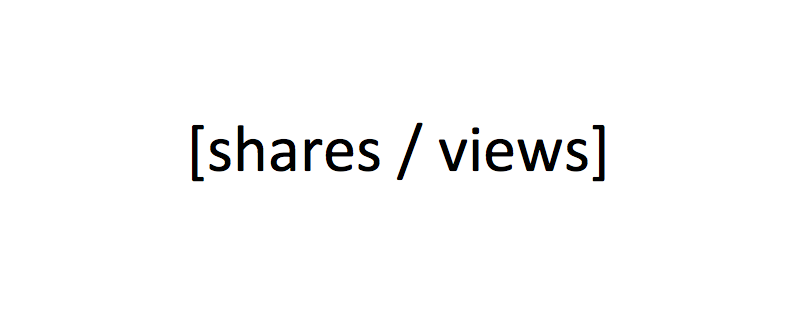There’s a lot of talk about shareable content and what it means to go viral. This post is in no means a guide to make sure content does go viral, with this post I hope to help people understand why content spreads and if that is really what has happened in the first place. The reason I think this matters is because marketers are judging other brand’s content to understand what worked and what didn’t hoping to replicate, but they aren’t necessarily always looking at the right data. And since I get into conversations related to this topic constantly, I figured it would be well worth sharing this idea of share rate here as well.
Enough for the introduction, I will use online video (ads) as an example, but the theory works for all kinds of online content, although the data sources will be different of course. There are two key numbers that people tend to look at when judging the succes of online video: views/impressions and shares, although I presume that’s already a distant second measure.
Youtube for instance has its own way to rate popularity of video ads, that is explained by themselves rated based on “an algorythm that factors in paid views, organic views and audience retention” – the Youtube Leaderboard. It’s unclear what the weight of each element is, but it’s clear that it’s mostly based around views. It is also the only number mentioned in the rating. As an outsider it’s difficult to judge only on that number what made each video succesful, was it the idea or was it the mediaspent? Knowing what Youtube’s business is about, there’s no need to explain why this rating makes sense for them.

So it’s important to look further. If you as a marketer (or agency creative) want to figure out why something worked views aren’t the best number to look at on its own. Unruly Media created another way to measure video by looking at the amount of time something was shared on social media. The ads chart is sponsored by Mashable, but you can also look at popularity of other video content. If you want to understand why content was spread amongst people it’s probably a good idea to check if it actually spread in the first place.
Here’s where it becomes interesting. The ranking based on shares looks pretty different than the one based on views, if you look at Youtube’s n2 for August for instance, you will see it’s almost impossible to find in the Unruly ranking. So it’s clear, you wonder how content spread? Look at the shares. But that’s not all.

Let’s look at a classic video we all know for instance: Evian Babies. With over 3 million shares that puts it at number 7 in the Unruly Viral Ads Chart of all time. Very succesful, but does that proof it was spread across social and hence a big succes? Not quite. Paid views will also generate shares – paid and organic. So we need to look beyond that. Here’s where the share rate comes in. The best way to judge whether a video was viewed because people shared it across the web is to look at the ration between views and shares. There’s a few ways to look at it, we use [shares/views] as the ratio, some use percentages, the idea remains the same.

Truly viral content such as ‘Dumb Ways to Die‘ or our own ‘Push to add drama‘ will have a share rate in between 1/20 and 1/10 or even higher (meaning 1/9 or 1/8 but you won’t see those number appear much). Evian Babies – to come back to that same reference – has a ratio of 1/40 and the other example I mentioned (Foot Locker – Youtube’s August n2) has a ratio of 1/200. I would reckon that everything below 1/15 (probably) or 1/20 (definitely) received some kind of ad push. The lower the number the more views were generated through advertising (versus organic) obviously.
The share rate on its own doesn’t say much either of course, a high rate with little views isn’t much of a succes. But if you really want to know why a video was seen by so many people then this is the measure you need to look at. Does that mean those other videos weren’t successful? Of course not. Is it wrong the push videos online with media? Ofcourse not. But want to understand where success came from with the little data you can access? Find the video on the Unruly chart (they show both views and shares – makes it easy) and calculate the share rate.
For the record, Youtube also has a kind of share ratio they use in their presentations but it’s not meaning the same thing. They will look at the ratio between paid views and organic views. Again, thinking of their business selling video ads, I makes for them to correlate paid versus organic views, rather than views versus shares as I suggested.
As mentioned in the beginning I used video to explain but this idea of share ratio counts for all types of content and thus should help you analyze success (or not) of others in good way.
(Please note that I only use examples to illustrate a point, it’s no judgement at all about the videos themselves).